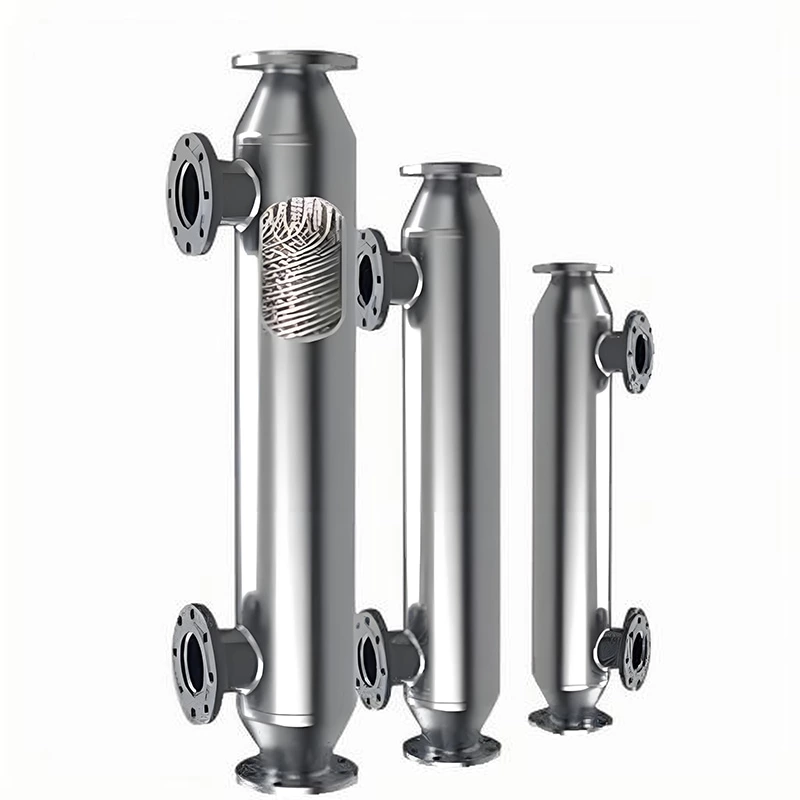
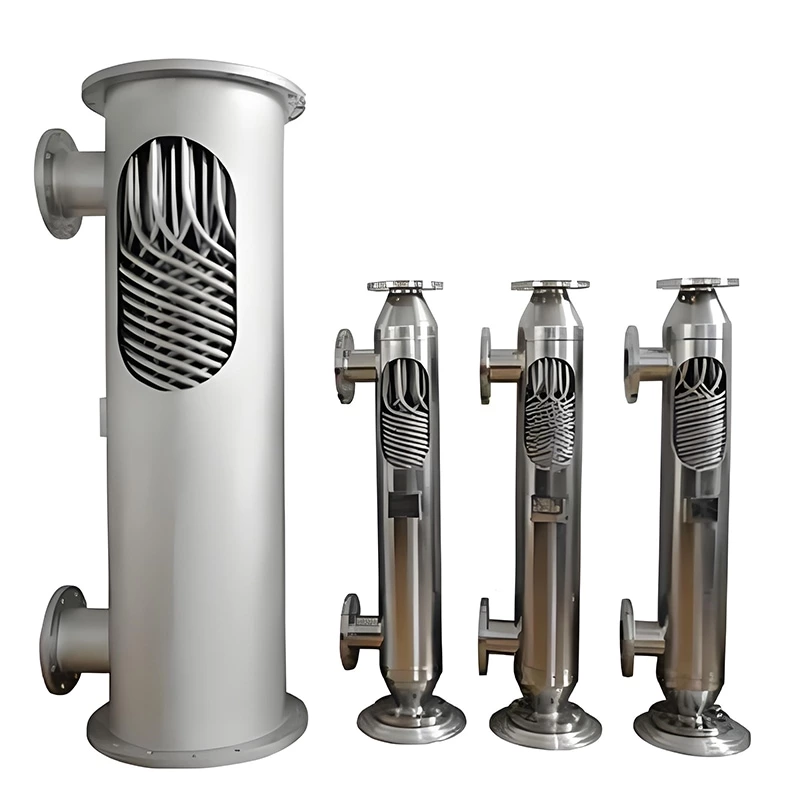
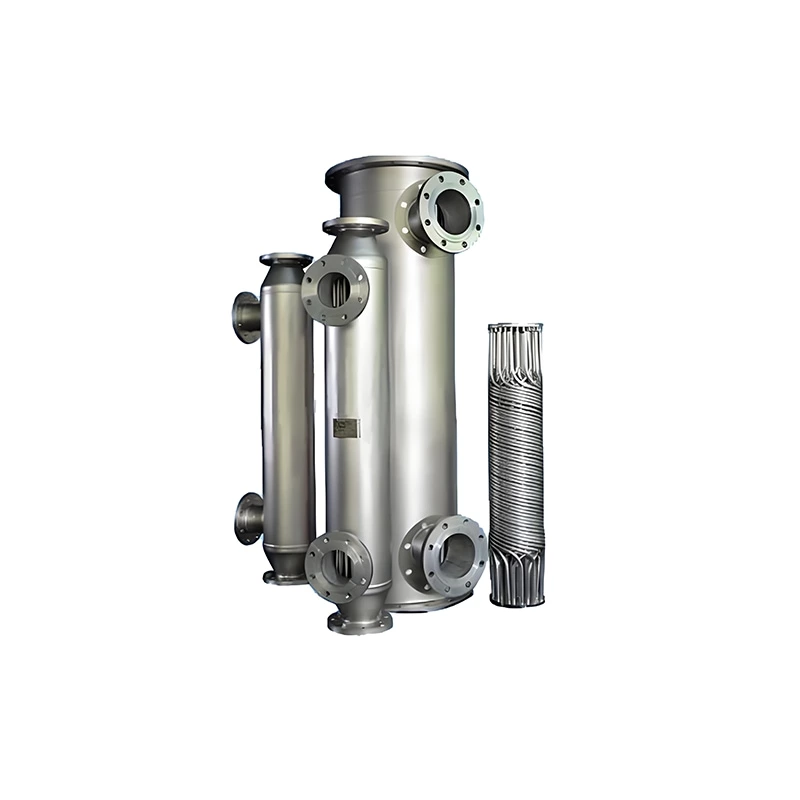
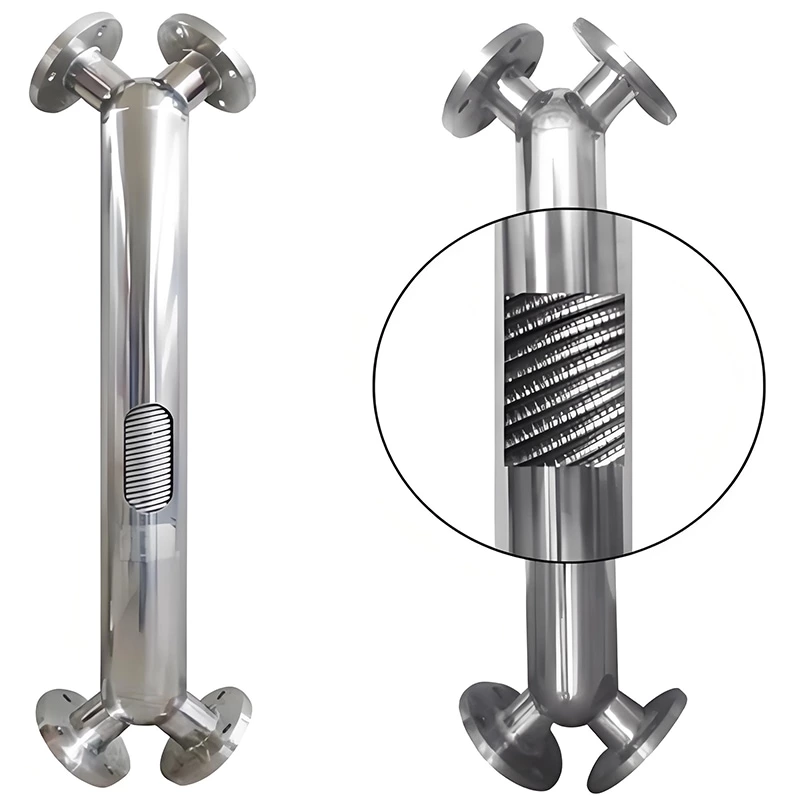
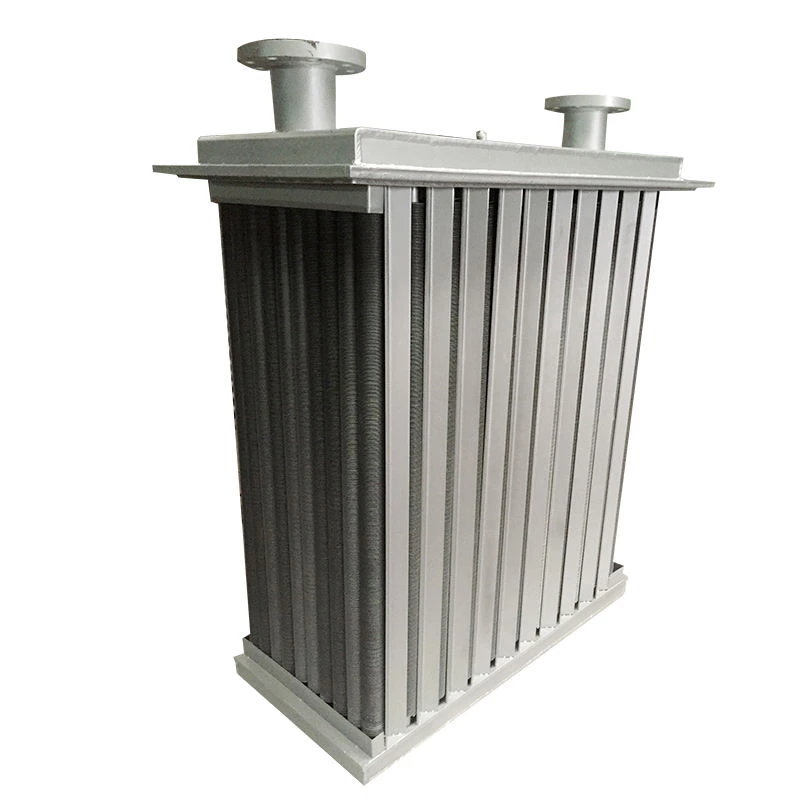
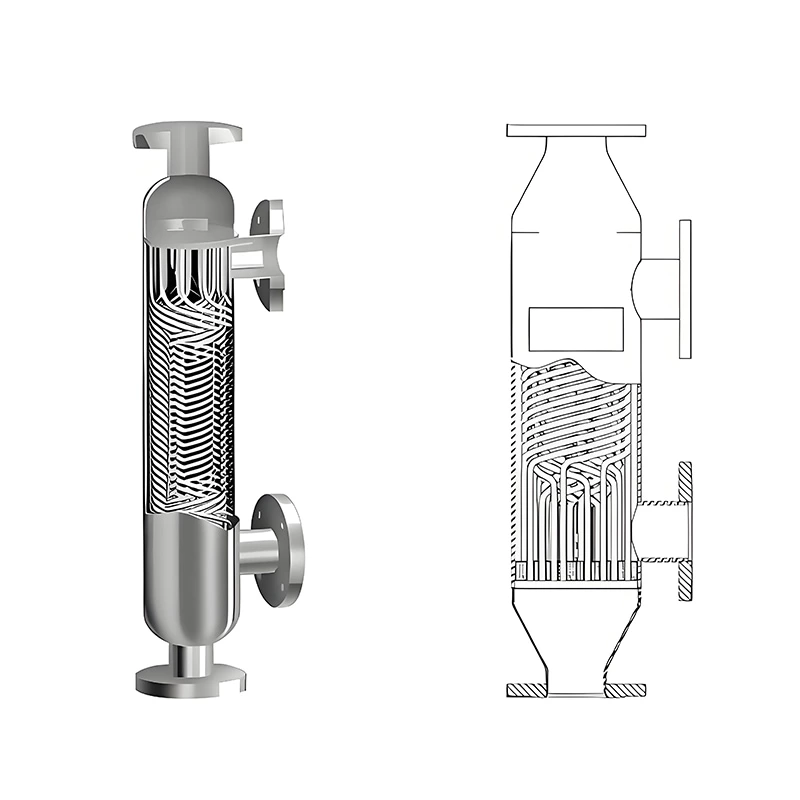
Wound Tube Heat Exchanger
A wound-tube heat exchanger is a highly efficient and compact shell-and-tube heat exchanger. Its core design involves alternately winding a series of slender heat exchange tubes around a central core in a spiral pattern, forming a coil. Typically, the tubes are arranged in multiple layers, with adjacent layers wound in opposite directions.
- Compact Structure: Due to its use of slender, tightly wound heat exchange tubes, it provides a large heat transfer area per unit volume. This makes it unparalleled in space-constrained applications, such as offshore platforms and chemical plants, and is typically several times more compact than traditional shell-and-tube heat exchangers.
- Extremely High Heat Transfer Efficiency: Spiral winding induces turbulence: As the fluid flows through the spiral tubes, centrifugal force creates secondary circulation, significantly disrupting the laminar boundary layer near the tube walls and enhancing heat transfer.
- High High Pressure Capability: The spiral winding structure imparts a certain degree of "elasticity" to the heat exchange tube bundle, enabling it to better compensate for stresses caused by thermal expansion, mechanical vibration, or pressure fluctuations. This makes it ideal for high- and ultra-high-pressure applications.
- High Vibration Resistance: The flexible structure and tight support of the tube bundle result in a high natural frequency, making it less susceptible to coupling with fluid-induced vibration frequencies, thereby effectively preventing vibration damage.
- High Anti-Fouling Resistance: The intense turbulence inside and outside the tubes prevents solid particles from depositing on the tube walls, creating a self-cleaning effect and slowing down fouling.