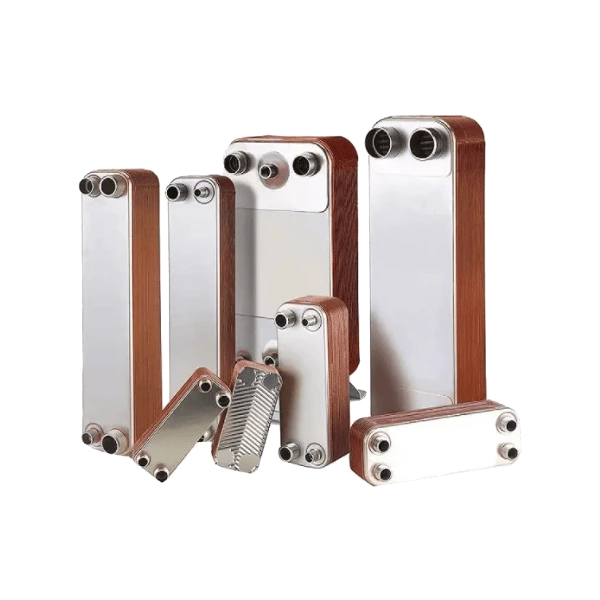
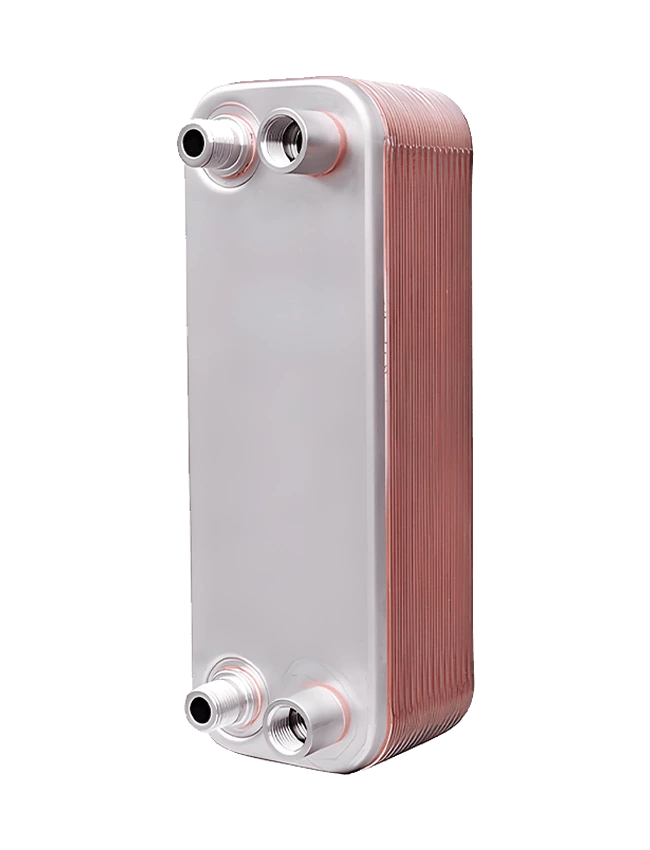
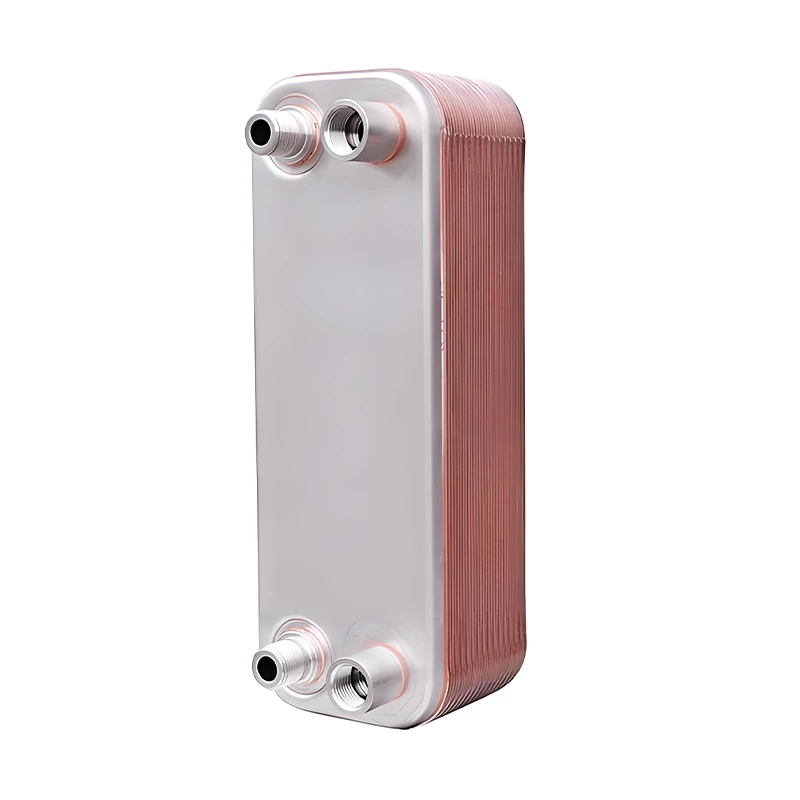
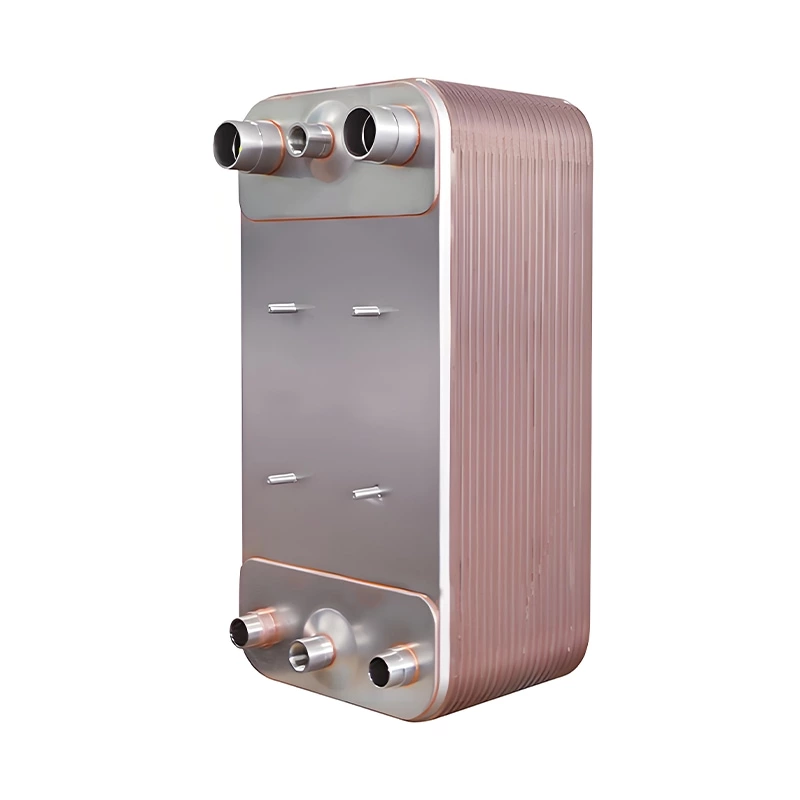
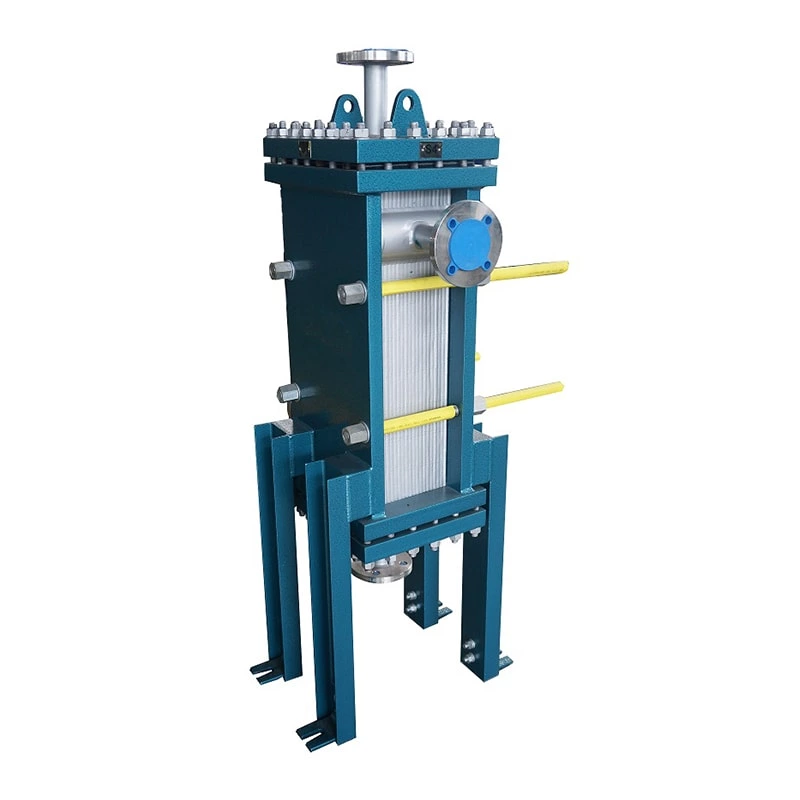
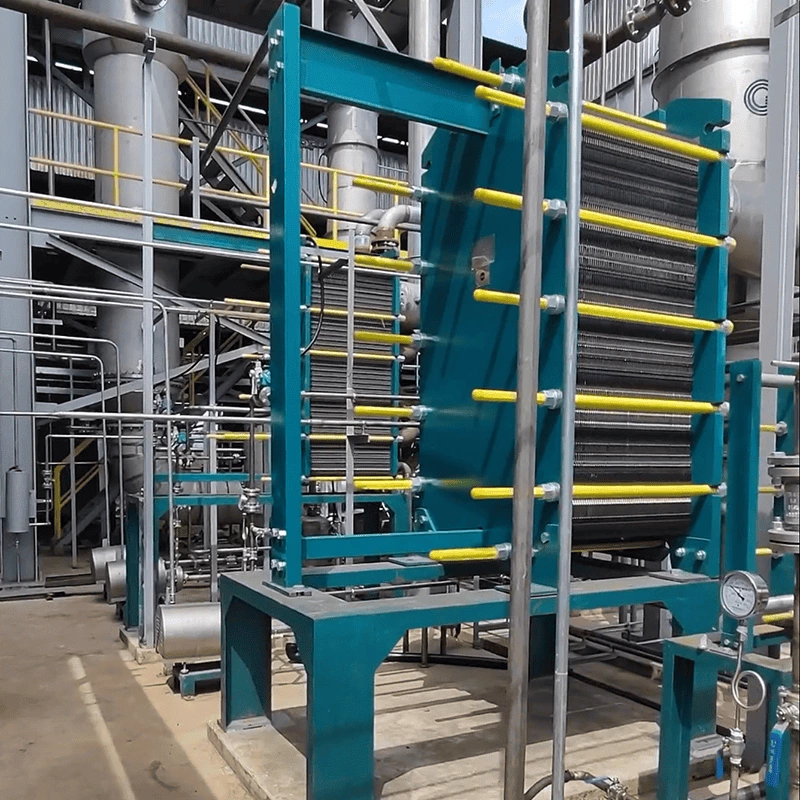
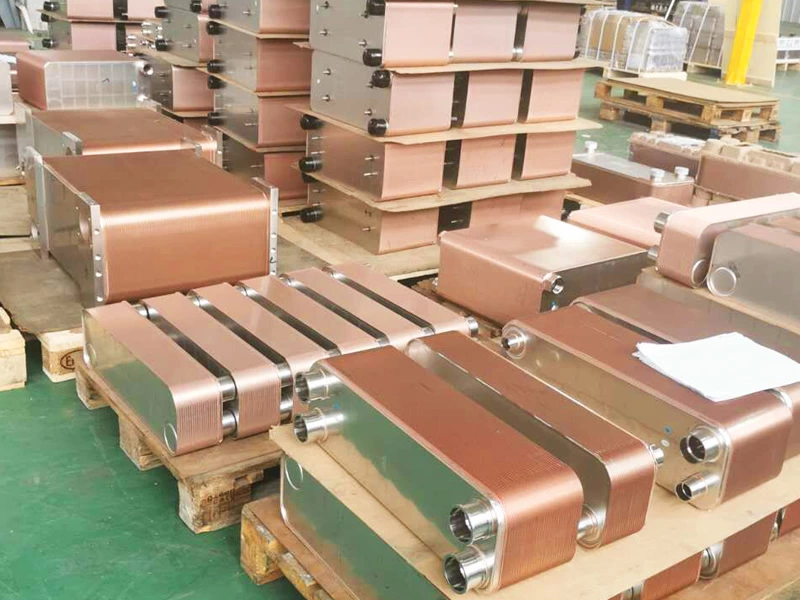
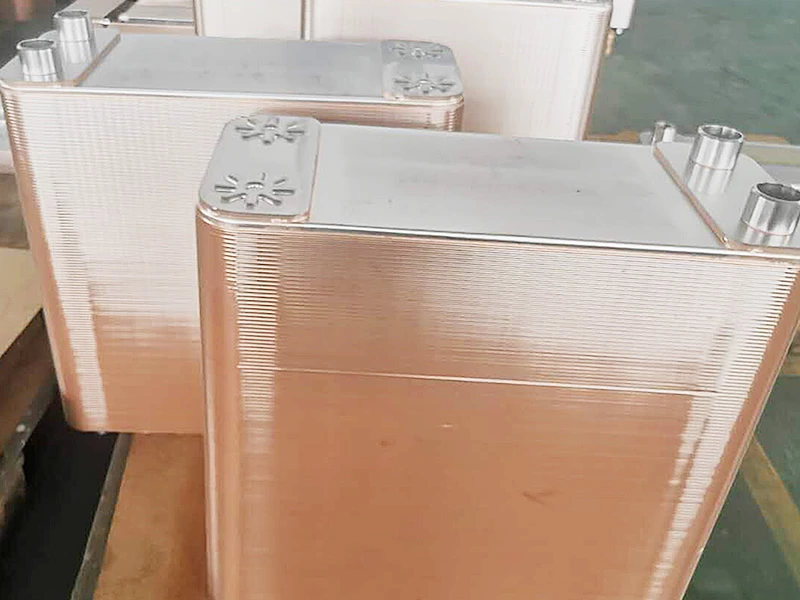
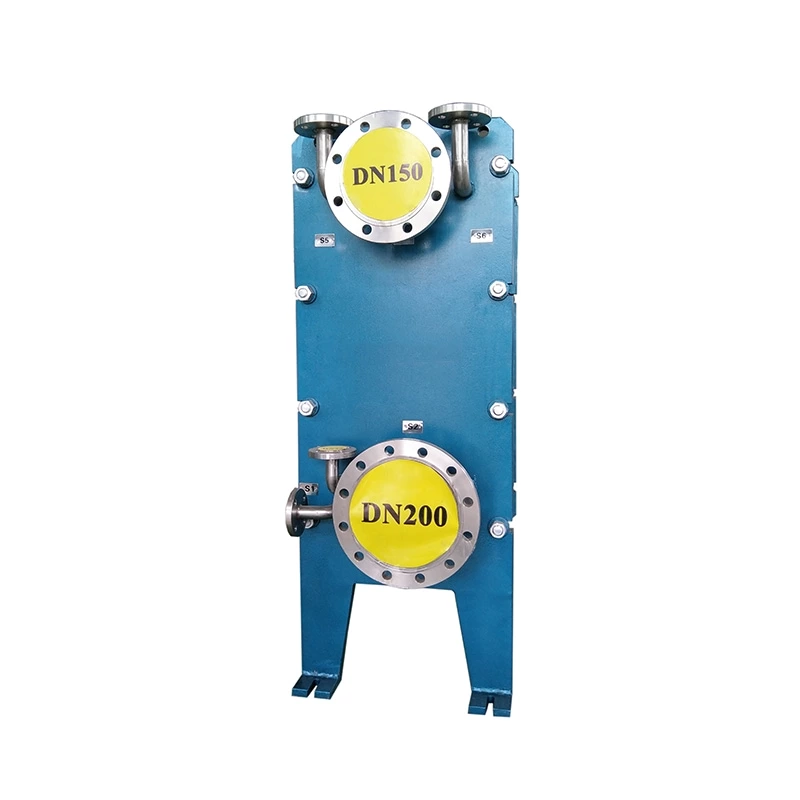
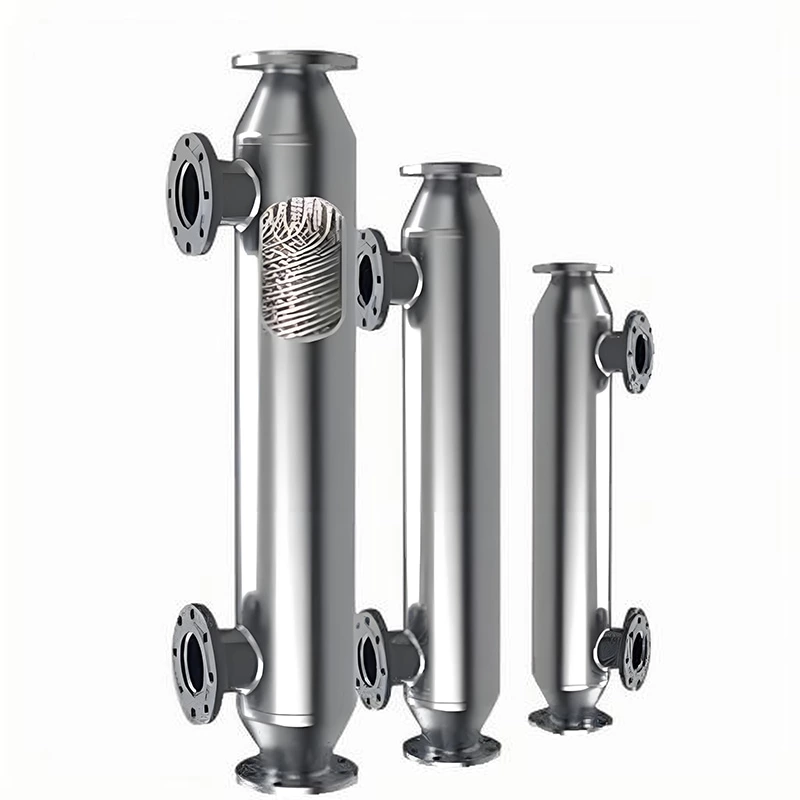
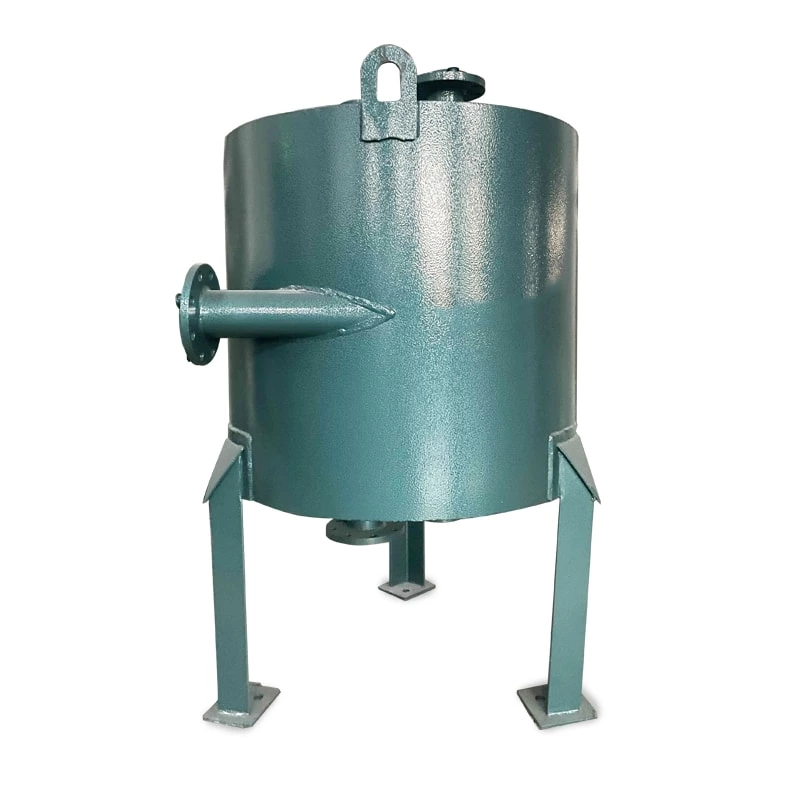
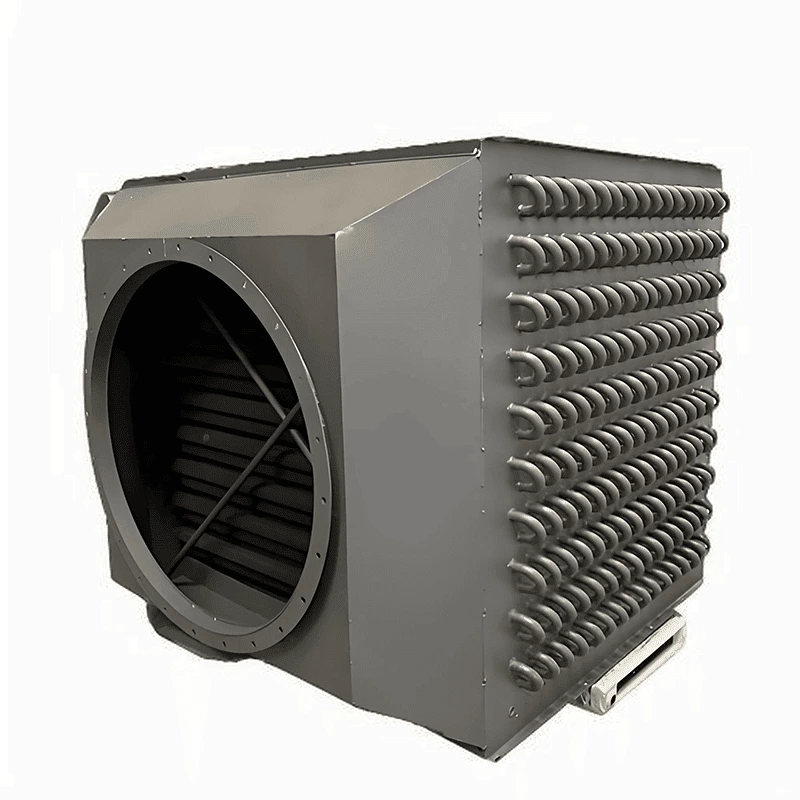
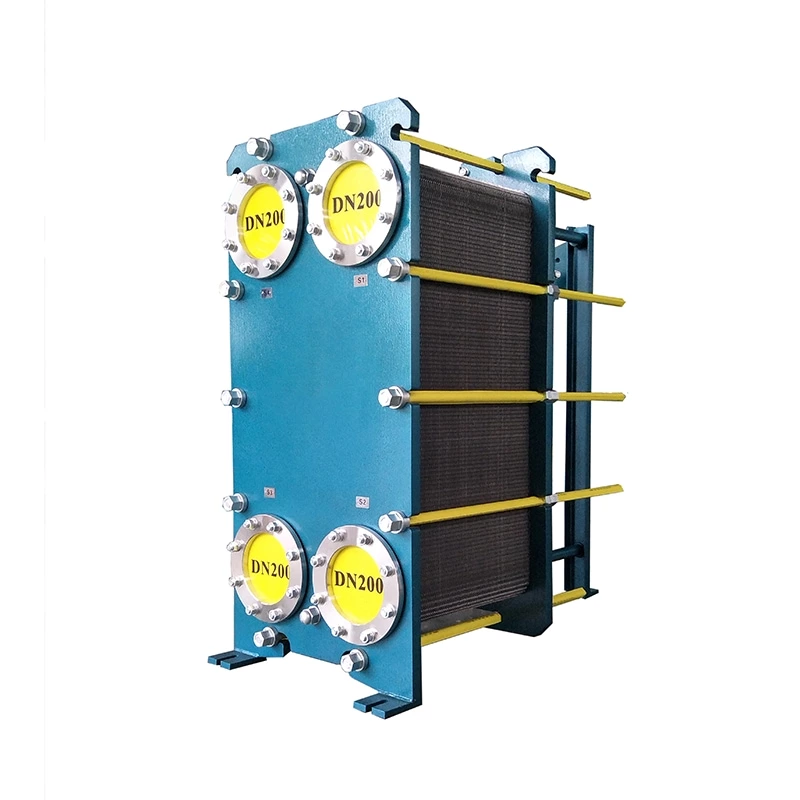
Welded heat exchangers are durable, high-performance solutions designed for processes involving extreme pressures, temperatures, or aggressive media. By eliminating gaskets and using fully welded plate or tubular structures, these exchangers ensure complete leak-tightness and exceptional mechanical strength. Each unit is engineered for optimal efficiency and reliability, combining compact design with superior thermal performance. This construction allows long service life and stable operation even in the most demanding industrial environments, including chemical, petrochemical, and energy applications.
Welded Heat Exchanger